Designing Flood-Resilient Agricultural Infrastructure
Agricultural infrastructure could be a safety net for crops regardless of location. What are the most effective and accessible installations to make as soon as possible in light of the advancing climate crisis?
Enhancing Resilience of Smallholder Farmers against Climate Change - Can Parametric Agricultural Insurance Make a Difference
To enhance the resilience of smallholder farmers against climate change, innovative solutions are urgently needed. One such solution is parametric agricultural insurance, a financial tool that has the potential to make a significant difference.
Highlighting Adaptive Practices for Climate Resilience in Agriculture
Climate resilience refers to the agricultural system's ability to recover from the impacts of climate change and even withstand them. This goes far beyond simply adapting to the new conditions.
Is Climate Change Impacting the Growth of Commercial Agriculture?
It is important to remember that technology should be viewed as a tool that can be used to optimize or improve the situation. What it isn't, however, is a free pass to continue implementing unsustainable practices.
Affecting Climate Change Through Farmland Relocation: 6 Considerations
Farming relocation is a concept that entails moving a country's farmland to a central location. The goal is to maximize crop yield while minimizing humans' negative environmental impact.
21 Acres -- Extreme precipitation threatens food security and drives up local food costs
Over the past decade, small local farms have been adjusting to increasing heat by switching out tried-and-true seed varietals for more heat-hardy varieties. By contrast, spring of 2022 has been unusually cold and wet-Seattle is experiencing its coldest spring since 1955.
Enhancing Climate Adaptation and Resilience in South Asia
Climate risks can directly affect crop production by reducing agricultural yields for some crops, increasing production volatility, and destabilising farmer incomes. On the one hand, oversupply could result in farmers receiving lower profits.
How Technology Can Bolster Farm Resilience to Shifting Temperatures
Maintaining abundant crop yields can effectively shrink society's starvation rate. Targeting greenhouse gas emissions and adverse field effects can increase global food security.
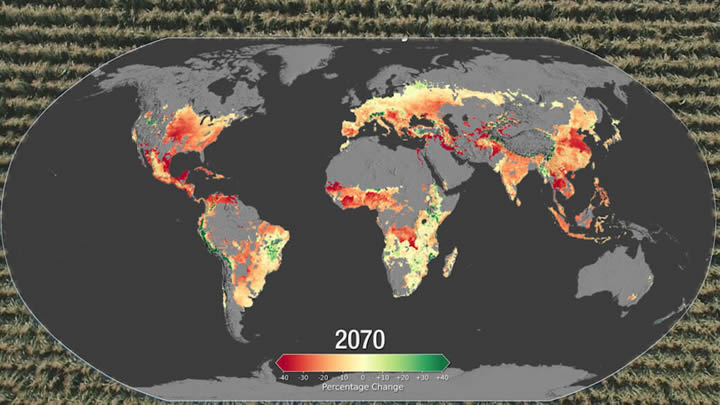
Global Climate Change Impact on Crops Expected Within 10 Years, NASA Study Finds
Climate change may affect the production of maize (corn) and wheat as early as 2030 under a high greenhouse gas emissions scenario, according to a new NASA study published in the journal, Nature Food.
Hedging Against Climate Uncertainty with Controlled Growth Environments
Global warming and climate uncertainty are making traditional farming increasingly unpredictable. But there is a solution - hedging against climate uncertainty with Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA), from traditional greenhouses to vertical farming.
Smart Solutions Help Farmers Combat Climate Change
As farmers learn to adapt to a changing climate, the industry must also reduce its own carbon intensity by 2030 in alignment with the Paris Agreement to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The Promise of Indoor, Hurricane-Proof 'Vertical' Farms
Meagan Flynn for The Atlantic: They might be an efficient way to produce food in a world with more-extreme weather-but only if growers can figure out a successful business model.
Records 1 to 12 of 12
Featured Product

igus® - Free heavy-duty plastic bearings sample box
The iglide® heavy-duty sample box provides a selection of five unique iglide bearings, each suitable for use in heavy-duty equipment due to their self-lubricating, dirt-resistant properties. Each bearing material boasts unique benefits and is best suited for different application conditions, though each can withstand surface pressures of at least 11,603 psi at 68°F.

.jpg)

.jpg)




(2).jpg)